FISHLESS AQUARIUM CYCLE
Of the seemingly endless debates within the aquarium hobby, there is one topic that stirs little controversy. Nitrifying bacteria is good. While the benefits of stable nitrifying bacteria are undisputed, there is some discussion of the best way to achieve and maintain a healthy microbiome. In this thread we will be looking at the “fishless cycle” method of bacterial culture in the marine aquarium.
 View attachment 4228
View attachment 4228
Of the seemingly endless debates within the aquarium hobby, there is one topic that stirs little controversy. Nitrifying bacteria is good. While the benefits of stable nitrifying bacteria are undisputed, there is some discussion of the best way to achieve and maintain a healthy microbiome. In this thread we will be looking at the “fishless cycle” method of bacterial culture in the marine aquarium.
-What is an aquarium nitrogen cycle?
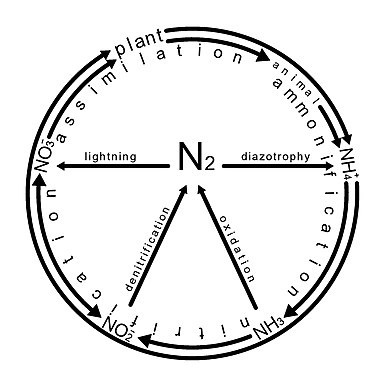
The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates through an aquarium ecosystem.
-Why is the aquarium cycle important?
A well-balanced tank contains organisms that are able to metabolize the waste products of other aquarium residents. This process is known in the aquarium hobby as the nitrogen cycle. Bacteria known as nitrifiers (genus Nitrosomonas) metabolize nitrogen waste. Nitrifying bacteria capture ammonia from the water and metabolize it to produce nitrite. Nitrite is toxic to fish in high concentrations. Another type of bacteria (genus Nitrospira) converts nitrite into nitrate, a less toxic substance. New aquariums often have problems associated with the nitrogen cycle due to insufficient beneficial bacteria.
The most common method of cycling an aquarium involves gradually increasing the population of fish over one to two months, allowing nitrifying bacteria time to grow and stabilize with the increase of biological waste. This method is usually done with a few hardy starter fish which have a higher chance of surviving the initial ammonia and nitrite spikes, whether they are intended to be permanent residents or to be traded out later for the desired occupants. Cycling marine aquariums with inexpensive fish such as damsels can be problematic, firstly because if you have already set the aquascape of your aquarium, trying to recapture the damsels can be very disruptive to substrate and potentially cause a spike in nutrients. If the damsels are left in the system, they can become territorial and cause drama with new fish additions. The struggle is real….

Nitrogen cycle - Wikipedia
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
-ADVANTAGES OF A FISH FREE CYCLE
The most significant advantage of fishless cycling is that it can reduce fish loss due to ammonia and nitrite spikes. Fish loss can be very discouraging for beginners of fish keeping, so indirectly, fishless cycling can also help beginners get a good start. Fishless cycling also allows the aquarium to be partially stocked from the moment it is cycled, if the nitrogen cycle is completed with an adequate concentration of ammonium chloride added daily. This makes stocking much faster than having to wait a few weeks between each new addition to the tank. Patience in the beginning can greatly pay off when the time comes to add fish.
Ammonium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula NH4Cl and a white crystalline salt that is highly soluble in water.
Solutions of ammonium chloride are mildly acidic. Aquarium specific products are available online and in some LFS.
-HOW TO CYCLE WITHOUT FISH
Before you embark on this mission, you will need a few things.
: Aquarium
: Water (At desired specific gravity)
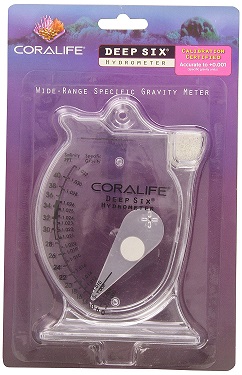
Coralife Deep Six Hydrometer - Aquarium Supplies - Test Kits
Cora life's Hydrometer takes a true water sample at six inch depth. Easy to read and accurate, this specific gravity meter is designed to give temperature-corrected readings in warm water aquariums. Includes a self-leveling, hanging device and allows your hands to stay dry, avoiding...
www.saltwaterfish.com
: Ammonia/Nitrite test kits https://www.saltwaterfish.com/product-red-sea-ammonia-test-kit-100-tests
: Filtration system

Eheim Pro 4+ Canister Filter - 600 - Aquarium Supplies - Filters
Pro4+ filter replaces the EHEIM Pro 3 range This new filter doesnt just boast a new sleek black color but it also has a Range Xtender Function As with most EHEIM filters, the Pro4+ comes complete with filter pads and media and all installation equipment.
www.saltwaterfish.com
: Ammonia
: Nitrifying bacteria seed colony https://www.saltwaterfish.com/product-nutrafin-cycle-biological-water-supplement-169-fl-oz
You are ready to begin your fishless cycle. Your aquarium has been set up and the filtration system is functioning properly and all carbon pads have been removed. Lets grow some funk! This is going to be the most simple direction possible. I am sure there are a million shade tree chemists who will be offended by my lack of hieroglyphic equations, and interstellar coordinates. Calm down scientists, take a deep breath, this isn't rocket surgery.
Step 1 - Seed the aquarium with beneficial bacteria, there are many commercial products available online here is a great example.

NutraFin Cycle Biological Water Supplement - 16.9 fl oz - Aquarium Supplies - Additives Phytoplankton Bacteria
Nutrafin Cycle Biological Aquarium Supplement features a high-concentration formula that immediately establishes a safe biological aquarium environment. Cycle goes to work fast, releasing massive amounts of beneficial bacteria that eliminate toxic ammonia and nitrites and creates a biologically...
www.saltwaterfish.com
If you have access to a well established aquarium, transplanting filter media from the established system into the new aquarium will do the trick. Keep in mind that you may be introducing any parasites and disease present in the host aquarium into your new aquarium. Using a good quality commercial bacteria product will bypass that risk. Use the product as directed for your aquarium volume.
Step 2 - Popular ammonium chloride products are typically in a liquid solution with a concentration of 50mg per litre You will want to add 4 drops per gallon of aquarium water.
Step 3 - Using a quality ammonia test kit. Test the aquarium water. You are looking for a concentration between two and four parts per million. A concentration above 5 ppm will kill your newfound micro friends and your cycle will fail. Test the water every 24 hours and wait to see the ammonia reading drop. At this point the filter contains bacteria that break down ammonia into nitrite, so the cycle has commenced. Keeping a cycling diary is recommended so you can plot the changes/patterns emerging.
Step 4 - Add Ammonia source again. Continue to test ammonia every 24hrs.
Step 5 - Test the nitrite levels.Wait until the nitrite level drops It will be high for a few weeks continue to add ammonia to feed the bacteria in the aquarium daily. Nitrite is strange in that once it begins to drop it will continue to hold at a very low level until the full cycle process has taken place in the aquarium.
Step 6 - Once you have 0ppm of ammonia, 0 ppm of nitrite, and a nitrate reading, your tank is ready for fish!
Continue to add ammonia up until you add fish, you don't want to starve your microbe friends.
source/references
Starting A Fishless Cycle - Aquarium Fishless Cycle
Aquarium fishless cycles are one option many people turn too when starting their tanks. Aquarium fishless cycles are explained in this article by The Shrimp Farm
Fishless cycling - Wikipedia
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
Attachments
-
237.9 KB Views: 1,269
-
6.9 KB Views: 1,222